Injection molding is a versatile manufacturing process that transforms raw materials into intricate, high-volume components. There are several common types of injection molding processes like gas-assisted injection molding, metal injection molding, liquid silicone injection molding, etc. This article delves into the diverse world of types of injection molding techniques, exploring the key differences between these different types of injection molding. We’ll examine the unique advantages each approach, providing valuable insights for engineers, designers, and manufacturers seeking to optimize these types of injection molding.
1. Gas-assisted Injection Molding
Gas-assisted injection molding is one of the famous types of injection molding process that creates solutions that effectively manufacture hollow components such as storage containers and automotive instrument panels. By injecting nitrogen or another inert gas into the mold, designers can create areas without adding weight to the final product. This process is now being adopted in different industries where cost efficiency and lightweight products are the end goal.
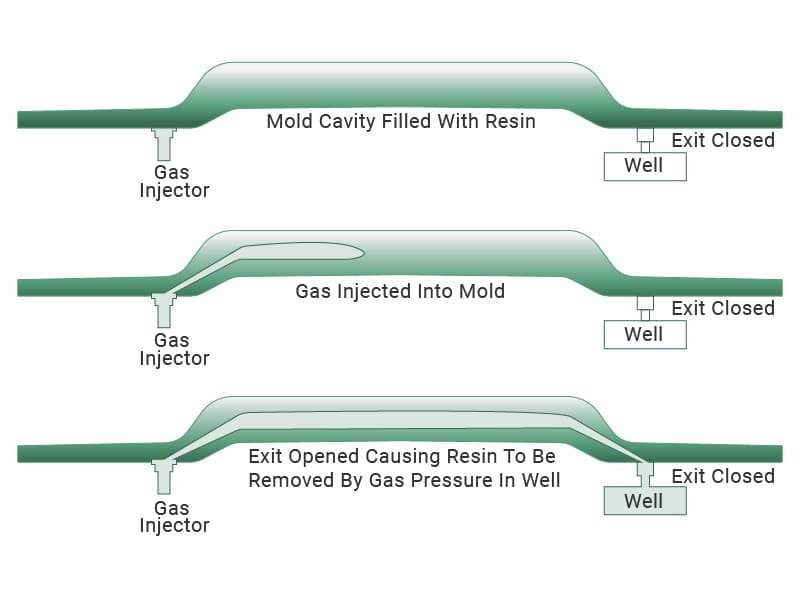
Advantages of Gas-assisted Injection Molding
- Lightness and cost-effectiveness: Gas-assisted injection molding produces lighter parts, making it highly suitable for the automotive and aerospace sectors.
- Eliminating sink marks: The gas ensures pressure distribution, minimizing sink marks.
- Enhanced aesthetics: Reduced material consumption leads to a surface finish.
2. Water-Assisted Injection Molding
Another common types of injection molding is water-assisted injection molding, it uses a pressurized stream of water to hollow out sections of a part during the molding process. This technique is an evolution of gas-assisted molding, providing superior cooling and hollowing for certain designs. It is particularly useful for creating parts with uniform wall thicknesses or hollow structures.
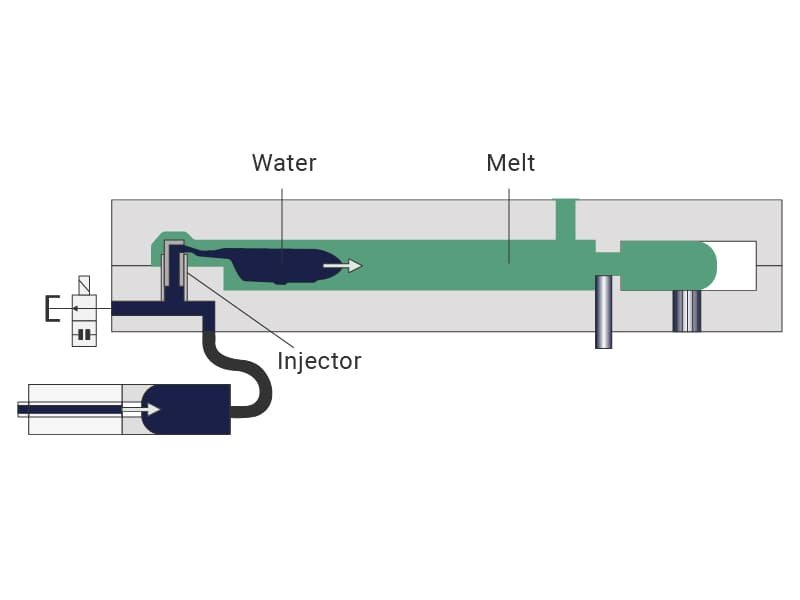
Advantages of Water-Assisted Injection Molding
- Efficient Cooling: Water’s superior thermal conductivity accelerates cooling, reducing cycle times and improving productivity.
- Lightweight Parts: Creates hollow sections in components, reducing weight without compromising strength.
- Material Efficiency: Reduces material usage in hollowed areas, saving costs and enhancing sustainability.
- Improved Surface Quality: Produces parts with smoother internal and external surfaces compared to other hollowing methods.
- Complex Geometries: Ideal for manufacturing intricate designs, such as automotive components and pipes.
3. Thin-wall Injection Molding
Thin-wall injection molding is known for manufacturing lightweight components. This technique focuses on creating delicate parts with a wall thickness, which brings significant benefits. Thin wall injection molding is a method that relies on accuracy and efficiency.
The decreased wall thickness of the molded part enables cooling, resulting in production cycles. This process is widely adopted in the consumer electronics and packaging industries, where lightweight, cost-efficient, and visually appealing components are necessary.
Advantages of Thin-wall Injection Molding
- Weight reduction: The result gives a lightweight finish, perfect for consumer electronics and packaging materials.
- Faster cycle times: It has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm, which allows faster cooling and high production capacity.
- Material savings: This usage of thin walls results in less material, which helps save the overall use of materials.
4. Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
When it comes to applications needing biocompatibility, flexibility, and durability to high temperatures, liquid silicone rubber injection molding is the solution.
LSR injection molding is a flexible and very accurate technique for producing items that must bear harsh environments. A two-part liquid silicone mixture is inserted into a mold during the process, and the final product is produced after it is cured.
Advantages of Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
- Biocompatibility: LSR is ideally used for manufacturing medical devices and implants.
- High heat resistance: It has the properties of biocompatible materials and works well in extreme temperatures.
- Enhanced flexibility: LSR molding enhances product flexibility, which can be used to manufacture reliable silicone cases.
5. Metal Injection Molding
Let us talk a little about metal injection molding – a process that produces complex metal pieces by combining metal powders with a binder. The automobile, aerospace, and gun industries all use this exact method.
The benefits of plastic injection molding are combined with metal’s strength and long-lasting ability throughout the process. Fine metal powders and a polymer binder are combined in the MIM process to provide a simple feedstock to inject into a mold. After the item is molded, the metal is sintered to create a solid piece after removing the binder.
Advantages of Metal Injection Molding
- Complex Made Easy: Easily produces metal parts that are a bit complex.
- Material utilization at its finest: The MIM process minimizes material wastage.
- Cost-effective solution: In comparison to metalworking, MIM offers cost-saving effectiveness.
- MIM has proven to be an important factor in the aerospace and automotive industries. It enables the production of complicated, lightweight, high-strength metal components while considering affordable costs.
6. Structural Foam Injection Molding
Structural foam injection molding is a specialized process where a foaming agent is mixed with the molten plastic resin before it is injected into the mold. As the plastic fills the mold, the agent creates a cellular core surrounded by a solid outer skin. This technique produces lightweight yet highly durable parts, ideal for large-scale applications requiring strength without excessive weight.
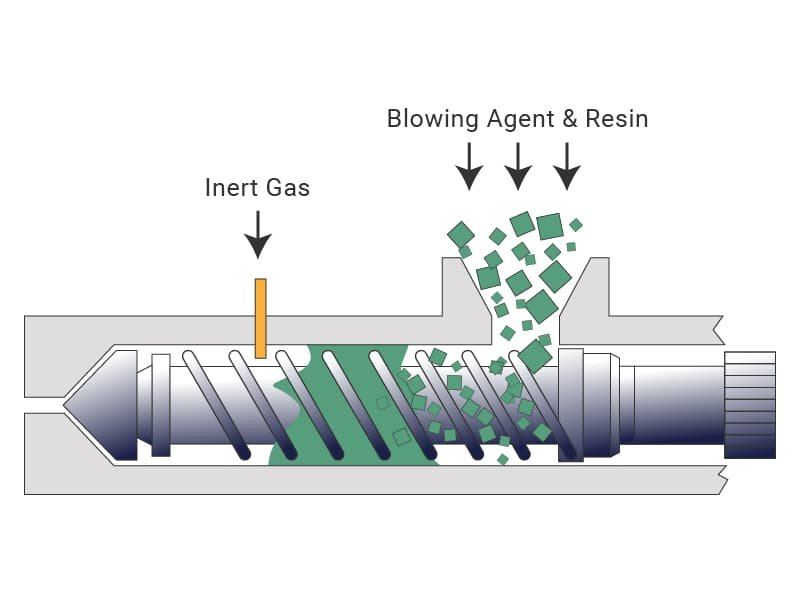
Advantages of Structural Foam Injection Molding
- Reduced Weight: The foamed core significantly reduces the overall weight of the molded part while maintaining its structural integrity.
- Enhanced Strength: The solid outer skin provides excellent durability, making it suitable for heavy-duty uses.
- Material Savings: Lower material consumption compared to traditional injection molding due to the cellular structure.
- Design Flexibility: Ideal for producing large, intricate parts with a balance of rigidity and weight reduction.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduced material use and lighter parts translate to lower production and transportation costs.
7. Micro Injection Molding
When discussing precision, the Micro injection molding process is your best choice. It involves manufacturing tiny parts with optimum precision, which is otherwise difficult to manufacture with other injection molding processes. It is best for different applications, including medical devices, microfluidics, and electronics.
With ever-increasing miniaturization demands, this technology has gained great importance in healthcare, electronics, etc.
Advantages of Micro Injection Molding
- Accuracy: Capable of producing tiny parts with high precision.
- Miniaturization: This is ideal for the compressed movement in technology.
- Minimizes material consumption: Lowers material expenses.
8. Reaction Injection Molding
Ever heard of the types of injection molding called reaction Injection molding? It involves mixing two reactive liquid components inserted into a mold to complete the process.
In this process, they undergo a chemical reaction that helps produce durable and lightweight components further used in the construction and automotive industry.
This type of injection molding provides a quality blend of robust and lightweight components. It works especially effectively in applications where maintaining structural integrity and reducing weight is essential.
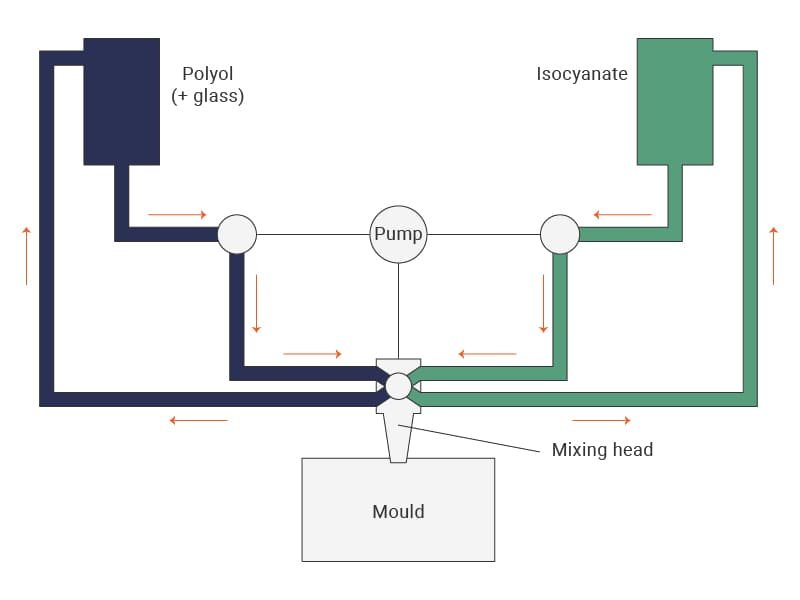
Advantages of Reaction Injection Molding
- Light as a feather: Compared to many other materials, RIM parts are lighter.
- Robust: Provides structural integrity for a range of uses.
- Optimal production capacity: Able to effectively produce large components.
9. Overmolding
Overmolding involves molding a second layer of material over an existing substrate or base part. The substrate can be a plastic component or a different material, such as metal. This process is often used to create multi-material parts, combining the strengths of various materials for enhanced functionality and aesthetics.

Advantages of Overmolding
- Improved Ergonomics: Commonly used to add soft grips or textures to tools and consumer products, improving usability.
- Enhanced Durability: Provides a protective layer that resists wear, impact, or environmental damage.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Allows for seamless integration of colors and textures, enhancing the product’s visual appeal.
- Cost-Effective Assembly: Combines multiple functions into a single part, reducing the need for secondary operations.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, including automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods.
10. Insert Molding
Insert molding involves placing a pre-fabricated component, such as a metal insert or threaded part, into the mold before the injection molding process. The molten plastic encapsulates the insert, creating a single cohesive part. This method is widely used for creating components with embedded hardware or multi-functional designs.
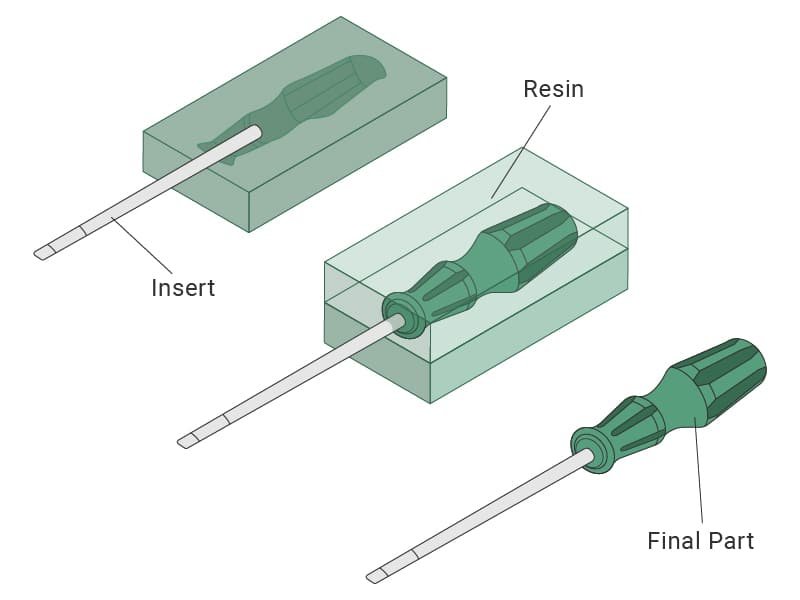
Advantages of Insert Molding
- Stronger Bonding: Provides a secure, permanent bond between the insert and the plastic, enhancing part reliability.
- Design Customization: Enables the creation of parts with complex configurations or additional functionality.
- Reduced Assembly Steps: Combines multiple parts into one, lowering production time and costs.
- Durability: Ensures inserts are firmly anchored, reducing the risk of loosening or failure under stress.
- Material Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of plastics and inserts, making it suitable for diverse industries.
Conclusion of Types of Injection Molding
Manufacturers use types of injection molding and its different procedures to enhance production, quality, and cost-effectiveness. It also provides a stream of opportunities for multiple industries. It is now considered the backbone of modern manufacturing as it offers a multi-faceted approach to lightweight manufacturing and affordable solutions.
The next time you use a daily life commodity, remember that injection molding is a critical process that shapes our environment. These revolutionized manufacturing processes have the sole vision of providing benefits to enhance productivity, reduce go-to-market time, and cost efficiency. With time, it is on the edge of becoming a widely used process in every industry.
FAQs about Types of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It is a high-volume production method ideal for creating complex shapes with precision. This process is highly efficient, cost-effective, and versatile, making it suitable for plastics, metals, glass, and elastomers.
There are several types of molding processes, the most typical and common types including:
- Injection Molding: For high-precision parts.
- Compression Molding: Used for thermoset plastics and rubber.
- Blow Molding: Ideal for hollow parts like bottles.
- Rotational Molding: Best for large, hollow shapes.
- Thermoforming: Heating plastic sheets to create shapes.
- Extrusion Molding: Produces continuous shapes like pipes.
There are many types of mold and can be categorized by number of cavities, mold materials, feeding systems, ejector systems, etc. The most common injection mold types including:
Molds can be categorized by cavity, runner systems, including:
- Single-Cavity Mold: Produces one part per cycle.
- Multi-Cavity Mold: Creates multiple parts simultaneously.
- Family Mold: Makes different parts in one cycle.
- Two-Shot Mold: Combines multiple materials in a single process.
- Hot Runner Mold: Reduces waste by keeping materials molten.
- Cold Runner Mold: Simpler and more cost-effective.
Take a deeper look at the mold types, read our blog What Are the Injection Mold Types.
Injection molding can be identified by several characteristics:
- Parting Lines: Visible on the surface where mold halves meet.
- Ejector Pin Marks: Circular marks left by ejector pins are used to push parts out of the mold.
- Consistent Wall Thickness: Ensures structural integrity.
- High Detail: Reflects the precision of the molding process. Examining these features can confirm the part’s manufacturing method.
While injection molding excels in mass production and precision, alternatives may be better depending on the application:
- 3D Printing: Ideal for prototyping and low-volume production with intricate designs.
- CNC Machining: Offers excellent material versatility and accuracy for low-volume runs.
- Compression Molding: Better for large, durable parts made from thermoset materials.The best method depends on factors such as design complexity, material, production volume, and budget.







