Precision China Injection Molding Service
We are a professional China Injection Molding Factory. We can provide you one-stop custom molding manufacturing worldwide.
- Afforable injection molding solution
- Precision injection mold
- DFM report for design analysis
- Material selection for specific requirement
- Secondary operation
- Assembly and testing
Precision Injection Molding Specifiactions
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Process Materials | Most plastics and rubber, including custom sourcing, see material list below |
| Standard Finishes | SPI and VDI |
| Press Sizes | 90 ~ 1100 tons |
| Mold Service | DFM report and mold flow analysis |
| Mold Ownership | Customer owned with mold maintenance |
| Mold Cavities | Single or multi-cavities |
| Mold Life | Unlimited (If the mold worn out, Erye will cover the cost of new mold) |
Additional Molding Options
Materials for Precision Injection Molding
ABS
PC
PA
PP
PMMA
POM
LDPE
HDPE
PVC
PTFE
PC/ABS
PS
TPE
TPE
TPV
Silicone
EPDM
NR
NBR
CR
SBR
IIR
FKM
FFKM
ABS
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
ABS Injection Molding is a manufacturing process where Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) plastic is melted and injected into a mold to create parts with high precision and strength. ABS is a tough, durable thermoplastic commonly used for products that need to withstand impact and stress, such as automotive components, consumer electronics, and household goods. The injection molding process ensures efficient mass production with consistent quality, offering versatility in design, easy post-processing (like painting), and a cost-effective solution for high-volume production.
The key advantages of ABS injection molding include its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and ease of customization. It is widely favored across industries for producing reliable, high-performance components.

PC
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC) material is a high-performance plastic widely used in injection molding for producing durable, transparent, and impact-resistant parts. Known for its excellent strength, optical clarity, and heat resistance, PC is ideal for applications requiring both mechanical durability and visual appeal. It is commonly used in industries like automotive, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods, where parts need to withstand high temperatures and physical stress.
Injection molding with PC offers advantages such as precise molding of complex shapes and tight tolerances, making it a preferred material for producing high-quality, intricate components.

PA
Polyamide
Polyamide (PA), commonly known as Nylon, is a highly versatile thermoplastic material used extensively in injection molding. Known for its excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength, toughness, and wear resistance, PA is ideal for producing durable parts in automotive, electrical, and industrial applications. It also offers good resistance to chemicals, oils, and abrasion, making it suitable for components that undergo continuous wear or operate in harsh environments.
In injection molding, PA allows for the creation of complex, high-precision parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional stability. Its ability to be reinforced with glass fibers or other additives enhances its strength and rigidity.

PP
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP) is a commonly used thermoplastic material in injection molding due to its lightweight, durable, and chemical-resistant properties. It is highly resistant to acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it ideal for applications in industries such as automotive, packaging, medical, and consumer goods. PP also offers low moisture absorption and excellent fatigue resistance, which contributes to the material’s longevity and reliability in various applications.
In injection molding, PP is easy to process, offering good flow characteristics and high molding efficiency. It can be molded into a wide range of complex shapes with fine details.

PMMA
Polymethyl Methacrylate
PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate), often referred to as acrylic or acrylic glass, is a transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity, UV stability, and high impact resistance. It is widely used in injection molding to create clear and durable components, making it ideal for applications in automotive, lighting, signage, medical devices, and consumer products.
In injection molding, PMMA can be processed easily, offering good flowability and the ability to create intricate, high-quality parts. It can be molded into complex shapes with precise detail and a glossy finish.

POM
Polyoxymethylene
POM (Polyoxymethylene), also known as acetal, is a versatile engineering plastic commonly used in injection molding for parts requiring high strength, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. It offers outstanding mechanical properties, such as high stiffness, durability, and resistance to wear. POM is also highly resistant to solvents, oils, and fuels, which enhances its reliability in demanding industrial environments.
In injection molding, POM allows for the production of complex, high-precision components with tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes. Its excellent flow characteristics make it easy to process, resulting in efficient production cycles.

LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene
LDPE is a widely used thermoplastic polymer characterized by its lightweight, flexible, and durable properties. LDPE is derived from the polymerization of ethylene monomers, resulting in a material that exhibits a low density of approximately 0.917 to 0.930 g/cm³, and has a relatively low melting point, making it easy to mold into a variety of shapes.
In injection molding, LDPE is ideal for producing parts like containers, bottles, films, and tubing. Its low-cost and ease of processing make it a popular choice for high-volume manufacturing.

HDPE
High-Density Polyethylene
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) is a versatile thermoplastic known for its high strength-to-density ratio, making it ideal for injection molding applications that require durability and resistance to impact. It has excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and can perform well in outdoor environments. These properties make HDPE suitable for manufacturing a wide range of products, including containers, bottles, automotive parts, and pipes.
In injection molding, HDPE is favored for its ease of processing and ability to produce parts with high stiffness and excellent impact resistance. It is highly efficient in mass production due to its fast cycle times and ability to be molded into complex shapes.

PVC
Polyvinyl Chloride
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a widely used thermoplastic material in injection molding due to its versatility, durability, and ease of processing. It comes in two primary forms: rigid and flexible. Rigid PVC is commonly used for pipes, fittings, and profiles, while flexible PVC is used for applications requiring elasticity, such as cables and flooring. PVC is resistant to chemicals, abrasion, and weathering, making it an ideal material for a broad range of industrial applications.
In injection molding, PVC offers excellent dimensional stability and the ability to mold complex shapes with high precision. It is highly cost-effective and can be easily processed, which makes it suitable for high-volume production.

PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance plastic known for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction properties, and high thermal stability. It is commonly used in injection molding for applications that demand superior performance in harsh environments, such as in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries.
In injection molding, PTFE can be challenging to process due to its high melting point and low flowability, requiring specialized equipment and techniques. However, once molded, PTFE components offer excellent durability, low friction, and resistance to corrosion and electrical conductivity.

PC/ABS
Polycarbonate/Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
PC+ABS (Polycarbonate + Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a versatile thermoplastic blend commonly used in injection molding due to its balanced combination of strength, durability, and ease of processing. The material combines the impact resistance and high strength of polycarbonate with the rigidity and ease of molding of ABS, making it ideal for applications that require both toughness and smooth surface finishes.
In injection molding, PC+ABS can be molded into complex shapes with tight tolerances and fine detail. The blend is widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, where durable yet lightweight components are necessary.

PS
Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a thermoplastic material widely used in injection molding for producing rigid, transparent parts with excellent clarity. It is known for its ease of processing, affordability, and ability to create intricate shapes with precise detail. PS is commonly used in applications where transparency is important, such as in packaging, disposable cutlery, and cosmetic containers, due to its crystal-clear finish.
In injection molding, PS is ideal for high-volume production of simple and lightweight parts. It offers good dimensional stability and can be easily molded into complex designs.

TPE
Thermoplastic Elastomer
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) is a versatile material that combines the flexibility of rubber with the ease of processing typical of plastics. It is known for its excellent elasticity, weather resistance, and ability to be molded at high temperatures. It is also recyclable, making it an eco-friendly choice for many applications.
In injection molding, TPE is a popular choice for producing parts that require soft-touch surfaces, impact resistance, and flexibility, such as seals, grips, and gaskets. Its thermoplastic nature allows it to be easily molded into complex shapes, offering excellent precision and cost-effectiveness.

TPE
Thermoplastic Polyurethane
TPU is a highly flexible and durable material known for its excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and impact resistance. It combines the processing advantages of thermoplastics with the elastic properties of rubber, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, including automotive parts, footwear, medical devices, and electronics. TPU offers good chemical resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and high wear resistance, which makes it suitable for both industrial and consumer products.

TPV
Thermoplastic Vulcanizate
TPV is a high-performance material that combines the processing ease of thermoplastics with the rubber-like properties of vulcanized rubber. TPV is created by blending vulcanized rubber particles with a thermoplastic resin, giving it excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to heat, oils, chemicals, and weathering. It is known for its high strength, good abrasion resistance, and low compression set, making it ideal for demanding applications such as automotive seals, gaskets, hoses, and electrical connectors. TPV’s ability to be processed using traditional thermoplastic molding techniques while maintaining the properties of rubber makes it a versatile material for a variety of industries.

Silicone
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is a highly flexible and durable material used in injection molding to produce a wide range of products. Known for its excellent heat resistance, flexibility, and electrical insulation properties, it is ideal for applications requiring high performance in extreme conditions. Silicone rubber maintains its properties even at high temperatures and resists aging, UV exposure, and ozone damage.
In injection molding, silicone rubber is commonly used to manufacture seals, gaskets, medical devices, and electrical components. Its unique combination of high elasticity and low compression set ensures long-lasting performance. The material is also biocompatible, which makes it suitable for medical and food-grade applications.

EPDM
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber is commonly used in injection molding due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. It remains flexible and durable even under extreme temperatures, ranging from -40°F to 275°F, making it suitable for a variety of automotive, electrical, and industrial applications.
In injection molding, EPDM rubber is used to manufacture seals, gaskets, and rubber components for high-performance applications. Its resistance to aging, water, and steam ensures long-lasting functionality, especially in outdoor and harsh environments.

NR
Natural Rubber
Natural Rubber (NR), is also used in injection molding for producing high-performance, flexible components. It boasts excellent elasticity, superior tensile strength, and resilience, making it ideal for applications that demand high stretchability and durability. NR exhibits outstanding wear resistance and is highly resistant to abrasion, which makes it well-suited for products subjected to repetitive stress and harsh environments.
In injection molding, NR is melted and injected into molds under high pressure, allowing for precise control over the part’s shape and dimensions. This process is ideal for manufacturing complex parts with intricate features and smooth surfaces.

NBR
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber
NBR commonly known as nitrile rubber, is widely used in injection molding due to its excellent oil, fuel, and chemical resistance. It offers superior mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and low compression set, making it ideal for applications in automotive, industrial, and sealing products.
In injection molding, NBR is heated to its molten form and injected into precise molds to create complex, durable parts with consistent dimensions. The material’s excellent molding characteristics allow for the production of intricate designs and high-precision parts, such as O-rings, seals, gaskets, and hoses.

CR
Chloroprene Rubber
CR is also known as Neoprene, is a synthetic rubber that offers excellent resistance to heat, oil, chemicals, and weathering. When used in injection molding, CR provides high flexibility and superior durability, making it an ideal choice for products exposed to harsh conditions. Its resistance to environmental factors like ozone and UV degradation further enhances its suitability for applications in automotive, industrial, and electrical industries.
In the injection molding process, CR is heated until it reaches a molten state, then injected into a mold cavity to form the desired shape. The material’s high-flow characteristics and ability to retain its properties under stress allow for the production of precise.

SBR
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber commonly used in injection molding for producing durable, high-performance parts. It offers excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and good aging properties, making it suitable for applications where toughness and long service life are required.
In injection molding, SBR rubber is used to create parts such as seals, gaskets, and automotive components. Its low-cost production process, combined with its strength and resilience, makes SBR a popular choice for a wide range of industrial applications.

IIR
Isobutylene isoprene rubber
IIR (Butyl Rubber) is a synthetic rubber renowned for its excellent impermeability to gases and moisture. It offers outstanding resistance to heat, UV light, ozone, and chemicals, which contributes to its longevity and reliability in harsh environments. Its excellent damping properties also make it suitable for applications requiring vibration absorption and noise reduction.
In injection molding, IIR butyl rubber is used to produce precise, durable parts like seals, gaskets, and flexible components. The material’s high elasticity and low compression set allow it to maintain its shape and functionality over time, even under extreme conditions.

FKM
Fluoroelastomer
FKM rubber (fluorocarbon rubber) is widely used in injection molding for applications requiring exceptional resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. It can withstand temperatures from -40°C to 250°C and offers outstanding protection against oils, fuels, acids, and solvents. FKM’s durability and high resilience ensure it performs well under extreme conditions, where other materials might fail.
In injection molding, FKM is often used to create precise, high-quality components such as seals, gaskets, O-rings, and other parts that require superior chemical and thermal resistance.

FFKM
Perfluoroelastomer
FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer) rubber is a premium material known for its exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and high-pressure environments. It combines the elasticity of rubber with the chemical and thermal resistance of fluoropolymers. FFKM remains stable even in environments involving strong acids, bases, solvents, and high temperatures ranging from -20°C to 325°C.
In injection molding, FFKM is used to create precision parts such as seals, gaskets, O-rings, and custom components that demand high performance and durability.


Injection Molding Guide
Injection Molding Surface Finishing
| Finishing | Description | Price Range | SPI Grades |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Provides a highly reflective surface, ideal for aesthetic applications such as consumer products. | $$$ | SPI A1, A2, A3 |

|
Offers a moderate sheen, balancing gloss and matte, suitable for parts needing some visual appeal without being overly shiny. | $ | SPI B1, B2, B3 |

|
Features a non-reflextive surface that reduce glare, often used for functional parts where aesthetics are less critical. | $$ | SPI C1, C2, C3 |

|
Enhances grip and durability, commonly applied to functional components to improve handling and reduce wear. | $$$ | SPI D1, D2, D3 |

SPI A: Glossy Finish
Provides a highly reflective surface, ideal for aesthetic applications such as consumer products.
- Price Range: $$$
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI A1, A2, A3

SPI B: Semi-Gloss Finish
Offers a moderate sheen, balancing gloss and matte, suitable for parts needing some visual appeal without being overly shiny.
- Price Range: $
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI B1, B2, B3

SPI C: Matte Finish
Features a non-reflective surface that reduces glare, often used for functional parts where aesthetics are less critical.
- Price Range: $$
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI C1, C2, C3

SPI D: Textured Finish
Enhances grip and durability, commonly applied to functional components to improve handling and reduce wear.
- Price: $$$
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI D1, D2, D3

Advantages of Injection Molding with Us
Precision and Quality Control
Flexible Production Capabilities
Material Expertise
Custom Injection Molding Applications
Injection Molding FAQs
The price of injection molding depends on several factors, including part complexity, material selection, mold design, production volume, and lead time. As we handle the entire process in-house, from mold making to large-scale production, we offer affordable injection molding serivce. Our mold fee starts at $500 while the unit price may vary from many factors. To get an accurate price quote for your specific project, we recommend discussing your design, materials, and production requirements with us.
Upload your drawing and get instant injection molding price!
The time it takes to make injection molding tooling can vary depending on your part's complexity and the project's specific requirements. Generally, we take 4 to 6 weeks to produce the production tooling, which includes the design and development process, adjustments after prototype testing, and finalization of the mold.
Our facility operates 24/7, ensuring quick turnaround for tooling production. Equipped with over 30 high-precision machining machines, we maintain high efficiency and consistency in mold creation.
Click and learn more about our injection mold service and capability.
Erye have more than 100 sets of machines for production. Generally each molding press allows for serveral hundreds of molded pars per day.
We will store the inactive mold for 3 three years and destroy the mold after you confirmation.
We believe in getting our customers the best possible parts the first time. Therefore, Erye does not charge for DFM report.
Related Resources of Injection Molding
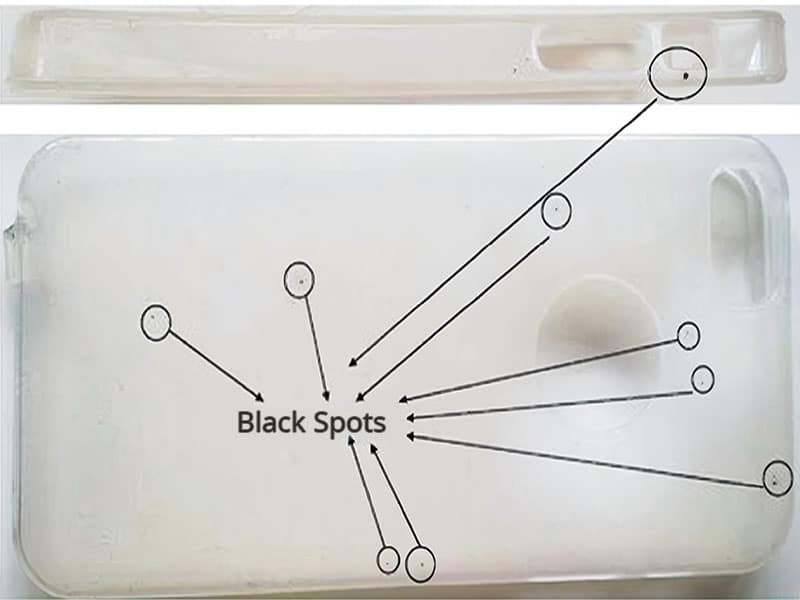
Black spots on plastic, and black specks are common visual defects in injection molding, appearing
Burn marks in injection molding appear as dark or black discolorations, often at the end
What is the Meaning of Warpage Plastic warpage deformation, often seen as twisting or distortion,